Published by Dr. Brandon Richland, MD

Botox, known scientifically as onabotulinumtoxinA, is a substance with a wide range of medical and cosmetic applications that has intrigued both the healthcare industry and the public alike. It is derived from a neurotoxic protein produced by the bacterium Clostridium botulinum.
This toxin has the unique ability to cause temporary paralysis by preventing the release of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine, which is responsible for muscle contraction. While this might sound alarming, the highly purified and diluted form used in Botox treatments is FDA approved and has been used safely for various purposes.
In the realm of cosmetics, Botox is celebrated for its ability to reduce the appearance of wrinkles and fine lines by relaxing the underlying muscles. However, its use extends far beyond the aesthetic; Botox is also employed in the medical field to provide relief for a range of conditions such as chronic migraines, excessive sweating, muscle spasms, and some bladder disorders.
Given its potency and potential risks, Botox injections should only be administered by qualified healthcare professionals.
Key Takeaways of What is Botox Made of?
- Botox is derived from a neurotoxin produced by Clostridium botulinum.
- It is used cosmetically to reduce wrinkles and medically for various conditions.
- Safe administration of Botox requires a trained healthcare professional.
Understanding Botox
Botox has a rich history and its uses have evolved over the years. The main component, botulinum toxin injection, has both medical and cosmetic applications.
What is Botox?
Botox refers to the drug onabotulinumtoxinA, an injectable substance derived from botulinum toxin. It’s known for its ability to temporarily paralyze muscles, which is useful in treating a range of medical conditions and for reducing wrinkles.
The protein in Botox comes from the bacterium Clostridium botulinum, and is carefully purified and diluted for medical use.
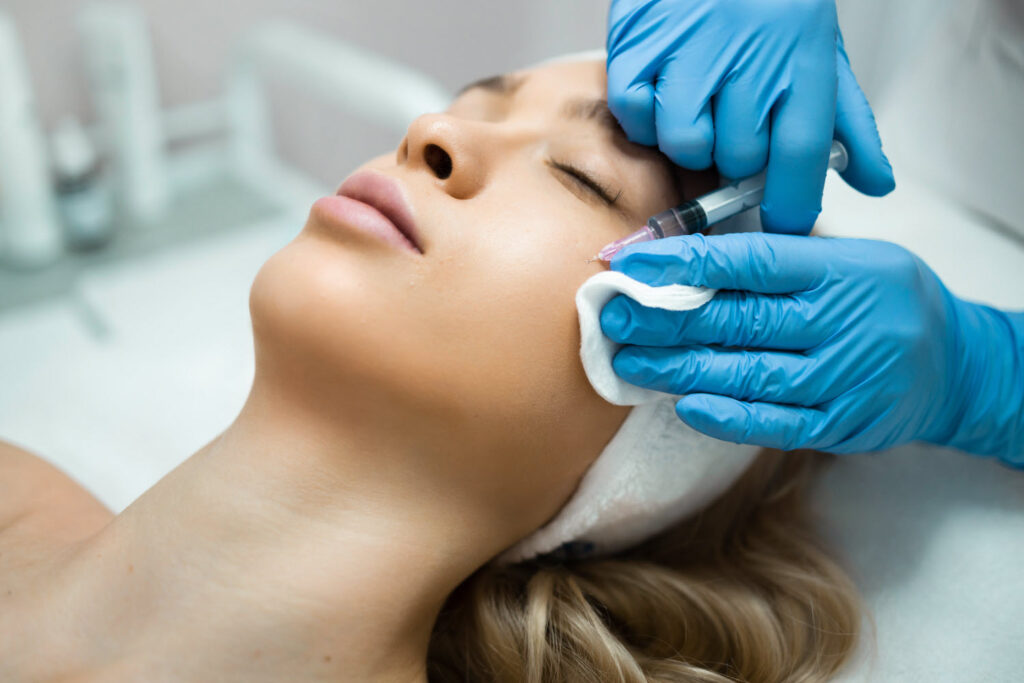
Botox Composition
Botox, a widely recognized brand name, owes its potency to botulinum toxin, a substance with both medical and cosmetic applications. The composition of Botox is crucial for its ability to temporarily paralyze muscles and reduce wrinkles.
Main Ingredients
Botulinum toxin is the primary active ingredient in Botox. It is a powerful neurotoxic protein derived from Clostridium botulinum, a bacterium found in the environment. In its purified medical-grade form, it is used to interfere with nerve signals in the body.
Formulations of Botox
Botox comes in a powder form that must be reconstituted into a solution for injection. Different formulations and strengths are tailored for specific conditions. For instance, the specific product onabotulinumtoxinA is designed for cosmetic use, whereas other formulations target various muscle spasticity disorders.
Botox Injections
Botox injections are a minimally invasive procedure known for their ability to reduce the appearance of facial wrinkles. They involve the precise application of a neurotoxic protein that temporarily paralyzes muscles.
Injection Procedure
The process involves a trained healthcare provider using a fine needle to inject a small amount of Botox into the targeted muscles of the face. Before the procedure, the skin may be numbed with a topical anesthetic to minimize discomfort. The procedure itself is quick, typically taking only a few minutes with no downtime required, allowing individuals to resume their normal activities shortly after.
Targeted Areas
Botox is most commonly applied to areas of the face where facial wrinkles are prominent. These include:
- Frown lines: The vertical creases that develop between the eyebrows.
- Forehead lines: The horizontal lines that form when one raises their eyebrows.
- Crow’s feet: The lines that fan out from the corners of the eyes.
Each of these areas responds well to Botox, resulting in a smoother, more youthful appearance that can last for several months before a subsequent treatment is necessary.
Medical Applications
Botox, a purified form of botulinum toxin, is renowned for its ability to smooth wrinkles, but it has significant medical applications as well. These uses leverage Botox’s ability to temporarily paralyze muscles by blocking nerve signals, addressing various health issues related to muscle activity and neurological disorders.
Chronic Conditions
Chronic Migraine: Patients who experience chronic migraines defined as having more than 15 headache days per month may find relief with Botox injections. Botox is FDA-approved for this purpose and can reduce the frequency of migraine attacks.
Overactive Bladder: For those struggling with an overactive bladder and symptoms like urgency and frequency, Botox may help in reducing these discomforts. It is injected into the bladder muscle, leading to better control and reduction of incontinence episodes.
Chronic Pain: Botox is also used to alleviate certain types of chronic pain. By relaxing muscles and preventing nerve signal transmission, it can ease pain associated with conditions that involve muscle tension or spasms.
Muscle Disorders
Cervical Dystonia: This painful condition causes involuntary muscle contractions in the neck, leading to abnormal movements and postures. Botox can alleviate these symptoms, offering patients relief from the discomfort caused by dystonia.
Muscle Spasms: Specifically for muscle disorders like strabismus (crossed eyes), blepharospasm (uncontrolled blinking), and limb spasticity, Botox injections can relax the contracted muscles.
Muscle Weakness: Although typically associated with causing muscle relaxation, Botox can actually help manage certain symptoms of muscle weakness by preventing muscle spasms that may contribute to the condition’s progression.
By targeting the nerves responsible for muscle contraction, Botox provides a therapeutic option for numerous conditions. Its precise application by licensed health care providers can bring significant improvement to the quality of life for patients with these medical issues.
Cosmetic Uses
Botox has become a household name for smoothing facial wrinkles and enhancing overall facial appearance. It is particularly known for its effectiveness and relative simplicity as a non-surgical cosmetic procedure.
Reducing Wrinkles
When it comes to combating the signs of aging, Botox Cosmetic is often used to reduce the visibility of facial wrinkles.
It works by temporarily paralyzing the muscles that contribute to wrinkles, thus smoothing the skin’s surface. Two of the most common areas treated are the glabellar lines, which appear between the eyebrows, and crow’s feet, which are the fine lines that fan out from the corners of the eyes.
Facial Aesthetics
Botox can also be used more broadly for facial aesthetics beyond just wrinkle reduction. It may be administered to soften lines around the mouth and on the forehead to maintain a more youthful and relaxed appearance. The precise application of Botox Cosmetic can improve the overall balance and symmetry of facial expression, further enhancing one’s appearance and boosting confidence.
Risks and Side Effects
While Botox is widely used for both cosmetic and therapeutic purposes, it is important that individuals are aware of the possible risks and side effects that may accompany its use. Side effects can range from mild, such as minor bruising at the injection site, to more serious allergic reactions.
Common Side Effects
Common side effects of Botox injections include:
- Pain, which may occur at the site of injection.
- Swelling or bruising, typically localized around the injection area.
- Flu-like symptoms, which can manifest shortly after the procedure.
- Muscle weakness, affecting muscles near the treatment area.
These side effects are usually transient and resolve without additional treatment.
Health Considerations
For individuals considering Botox, there are several health considerations to take into account:
- Allergic Reactions: Some people may experience allergic reactions, characterized by itching, rash, or hives. These reactions necessitate immediate medical attention.
- Serious Side Effects: In rare cases, Botox can cause more serious side effects. Symptoms of such adverse reactions should be reported to a healthcare provider immediately.
- Pregnancy: Pregnant women should exercise caution and discuss the risks of Botox with their healthcare provider.
- Pre-existing Conditions: Those with certain neurological or muscular disorders should inform their doctor prior to receiving Botox, as they may be at an increased risk for complications.
It is crucial that individuals receive Botox injections from a licensed and skilled health care provider to minimize the likelihood of negative outcomes.
Safety and Precautions
When considering Botox treatments, it’s essential to prioritize safety and adhere to recommended precautions. The FDA has approved Botox for cosmetic use, ensuring a standard of safety and effectiveness when administered by a licensed professional. However, individuals who are pregnant, breastfeeding, or have certain allergies must consult their healthcare provider before proceeding.
Usage Guidelines
The first step in the safe application of Botox involves understanding the Usage Guidelines. Botox should only be administered by qualified healthcare professionals who are well-versed in facial anatomy to avoid improper injection and complications.
- FDA Approval: Botox is FDA-approved for specific medical and cosmetic purposes.
- Client Evaluation: Prior to treatment, a thorough evaluation should be conducted to determine any history of allergic reactions or contraindications.
- Needle Safety: Only sterile, single-use needles must be used to avoid any risk of infection.
It’s also crucial for clients to disclose if they are pregnant or breastfeeding, as the safety of Botox has not been established for these individuals. Those with neuromuscular disorders or an allergy to any Botox component should not use this treatment.
Before and After Care
Proper care before and after Botox injections can help ensure the best results and reduce the risk of complications.
- Prior to Injection:
- Avoid alcohol for at least 24 hours before the procedure.
- Discuss the use of blood-thinning medications with the healthcare provider.
- Anesthesia: Typically, no anesthesia is needed, but a topical numbing cream may be applied to minimize discomfort.
- Post-Injection Care:
- Apply ice gently to the treated area to reduce swelling.
- Do not rub or massage the treated areas to prevent Botox from spreading beyond the intended region.
Clients should report any signs of an allergic reaction such as difficulty breathing, swelling, or hives to their healthcare provider immediately. Botox treatments require a balance between the desired cosmetic outcome and maintaining a high standard of safety and care.
Treatment Considerations
When considering Botox treatments, it’s important for individuals to discuss their health concerns and treatment goals with a qualified healthcare provider to establish suitability and likely benefits.
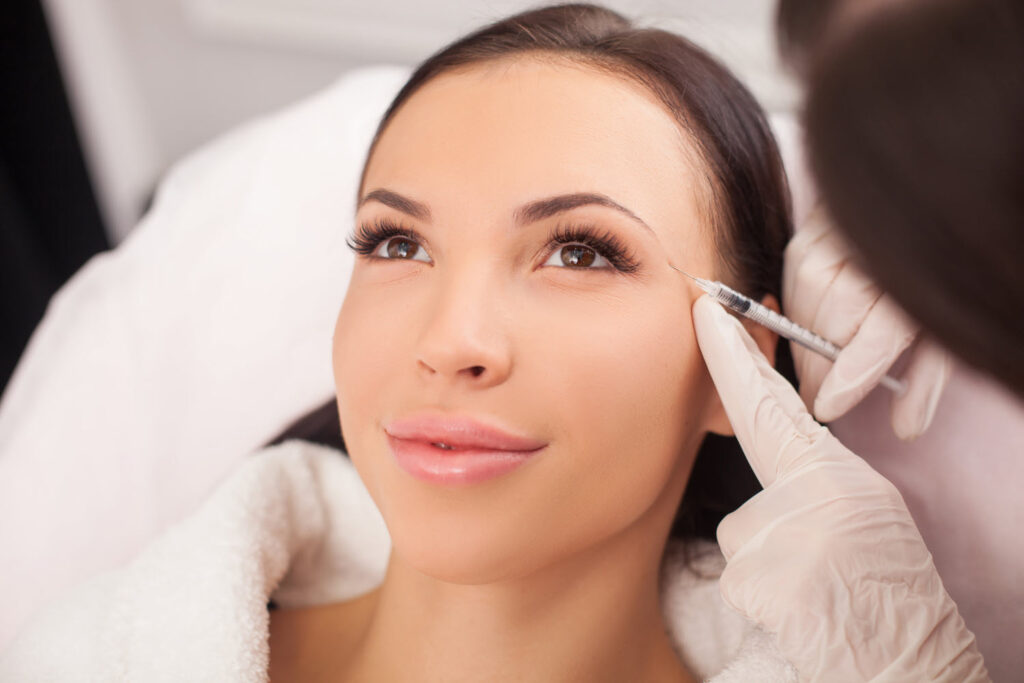

Determining Candidacy
Migraine Relief: Individuals experiencing chronic migraines, defined as headaches on 15 or more days each month, may be candidates for Botox injections. Botox can significantly reduce the frequency of migraine attacks.
Managing Overactive Bladder: Those facing issues with an overactive bladder often find that Botox helps in managing symptoms like urinary incontinence.
Hyperhidrosis Treatment: People dealing with excessive sweating, especially in the underarm area, may benefit from Botox’s ability to alleviate symptoms of hyperhidrosis.
Expectations and Outcomes
Effectiveness: Botox is known for its ability to temporarily paralyze muscles, leading to a decrease in muscle spasticity in various conditions, including muscle stiffness in the neck. It is crucial for individuals to have realistic expectations regarding the effectiveness and temporary nature of the treatment.
Maintenance: Treatment requires maintenance, as its effects typically last for around three to six months. Patients seeking relief from migraines, urinary incontinence, or hyperhidrosis should plan for regular follow-up sessions to sustain the benefits.
Comparative Treatments
When considering smoothing out wrinkles and lines, patients today have a variety of options to choose from, ranging from traditional Botox to newer alternatives and competitors. Understanding the differences and options available can help one make an informed decision for their skincare needs.
Alternative Procedures
Injectable Fillers: Unlike Botox, which is a neuromodulator that relaxes muscles, injectable fillers work by directly filling in wrinkles or plumping up areas that have lost volume over time. There are different types of fillers such as those made from hyaluronic acid or calcium hydroxylapatite. These fillers provide immediate results and can be used on various parts of the face including the lips, cheeks, and nasolabial folds.
Botox vs. Competitors
Botox (OnabotulinumtoxinA): The well-known Botox is FDA-approved for cosmetic uses such as treating forehead lines, crow’s feet, and glabellar lines. It’s also used for medical conditions including chronic migraines and excessive sweating.
Dysport (Abobotulinumtoxina): Similar to Botox, Dysport is designed for the temporary improvement of moderate to severe frown lines between the eyebrows. It’s known for spreading more which might require fewer injections in larger areas.
Xeomin (Incobotulinumtoxina): Unlike Botox and Dysport, Xeomin consists of a “naked” botulinum toxin, meaning it doesn’t contain any of the accessory proteins that Botox and Dysport have. It is considered a more purified form and can be beneficial for patients who have built up resistance to other neuromodulators.
Myobloc (RimabotulinumtoxinB): A notable trait of Myobloc is its use of a different botulinum toxin type which can make it an option for individuals not responding to type A products.
Jeuveau (Prabotulinumtoxina): The newest addition to the list, Jeuveau is exclusively for aesthetic purposes and is also referred to as “Newtox”.
Each product has its onset time, duration of effect, and unique properties which influence a practitioner’s recommendation for a patient’s specific concerns. Choosing the right product often depends on the area being treated, the desired effect, and individual response to neurotoxins.
The Science of Botox
Botox derives from a potent neurotoxic protein known as botulinum toxin, which is carefully harnessed in medicine, and can have beneficial effects on the nervous system.
Mechanism of Action
Botulinum toxin works by targeting the nervous system to disrupt the normal signaling processes that stimulate muscle contraction. The toxin prevents the release of acetylcholine, a key neurotransmitter, at the nerve endings. This action is essential to its therapeutic effects, as it temporarily paralyzes muscles, which can be useful in treating various conditions that involve overactive muscle activity.
Neurological Effects
The neurological effects of Botox are specific to the muscles into which it is injected. By inhibiting the release of acetylcholine, botulinum toxins reduce abnormal muscle contraction, leading to a temporary improvement in related conditions. This selective action on the nervous system is what allows for controlled use, despite the potent nature of the toxin.
Frequently Asked Questions About What is Botox Made of?
1. What’s The Main Component Found in Botox Treatments?
The primary ingredient in Botox is a purified form of botulinum toxin type A, also known as onabotulinumtoxinA, which is derived from the bacterium Clostridium botulinum.
2. Are There Any Animal-Derived Ingredients in Botox?
No, Botox does not contain any animal-derived ingredients. It is primarily made up of neurotoxins produced by the bacterium Clostridium botulinum.
3. Can You List The Harmful Substances That Might Be Present in Botox?
The use of Botox is generally considered safe when administered by a qualified healthcare provider. However, it may cause some side effects like bruising and minor swelling.
4. Is The Origin of Botox Considered Natural or Synthetic?
Botox is derived from a naturally occurring bacterium, Clostridium botulinum. The toxin itself is produced naturally by the bacteria before being purified for medical use.
5. How Does Botox Affect The Skin?
Botox temporarily paralyzes muscles, which can result in the reduction of wrinkles on the skin for a smoother appearance.
6. What Should I Know About The Safety of Botox?
Botox injections are FDA-approved and are safe when carried out by trained professionals. It is critical to follow the guidance of a healthcare provider to minimize risks and ensure the effectiveness of the treatment.

Conclusion and Summary of What is Botox Made of? Ingredients Behind This Cosmetic Treatment
Botulinum toxin injections, widely recognized as Botox, are a cornerstone in both therapeutic and cosmetic treatments, utilizing botulinum neurotoxins to target facial muscles effectively. These injections work by blocking neuromuscular transmission, which relaxes muscles and reduces the appearance of facial wrinkles, particularly in the frontalis and lateral orbicularis oculi muscles.
This mechanism involves the toxin binding to the nerve terminal, preventing the release of acetylcholine from vesicles, thereby decreasing muscle activity at the injection sites.
The use of botulinum toxin therapy extends beyond cosmetic applications to treat medical conditions such as cerebral palsy, myasthenia gravis, and severe underarm sweating. This broad utility is due to the toxin’s ability to provide targeted relief from excessive or unwanted muscle contractions.
However, it’s essential to manage the doses carefully, as multiple injections or higher doses can lead to complications like antibody formation. Patients injected serially with botulinum toxin may develop neutralizing antibodies, reducing the treatment’s effectiveness and leading to issues like neck weakness or eyelid ptosis.
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates the use of botulinum toxin, ensuring its safety and efficacy for both cosmetic and therapeutic purposes. As Botox treatment continues to evolve, it is paired increasingly with dermal fillers for more comprehensive facial rejuvenation, enhancing both facial structure and expression.
Please note that this article is intended for informational purposes only and should not be construed as medical advice. Before making any changes to your treatments, please consult with your healthcare provider to discuss the appropriateness and safety of such changes.
Ready For Your First-Class Cosmetic Experience in Orange County (OC) California (CA)?
Are you located in one of these Orange County (OC) / Southern California cities?
Aliso Viejo, Anaheim, Brea, Buena Park, Costa Mesa, Coto de Caza, Cypress, Dana Point, Fountain Valley, Fullerton, Garden Grove, Huntington Beach, Irvine, La Habra, La Palma, Laguna Beach, Laguna Hills, Laguna Niguel, Laguna Woods, Ladera Ranch, Lake Forest, Los Alamitos, Mission Viejo, Newport Beach, Orange, Placentia, Rancho Santa Margarita, San Clemente, San Juan Capistrano, Santa Ana, Seal Beach, Stanton, Tustin, Villa Park, Westminster, or Yorba Linda?
Plastic Surgeon Dr. Brandon Richland, MD and our Cosmetic Aesthetics Team are ready to help you look and feel your absolute best.
Elevate your confidence and self esteem levels to unfathomable new heights!
Schedule your in-person consultation in our modern and luxurious offices in either Fountain Valley, CA (Main HQ) or our Newport Beach, CA office.
Do you live outside of Southern California or short on time? For your convenience, Virtual Consultations are also available.
Our warm and engaging Team of carefully selected Aesthetics Professionals will make you feel calm, cool, collected, and right at home throughout your entire consultation and surgery process.
Schedule Your Aesthetics Consultation here, or call us directly at 949-867-4496 today.
About the Author

Dr. Brandon Richland, MD is a respected Board Certified Licensed Plastic Surgeon in Orange County / Southern California specializing in cosmetic and reconstructive surgeries.
Driven by his passion for medicine, Dr. Richland obtained his Doctor of Medicine (M.D.) degree from the prestigious program at Saint Louis University (SLU) School of Medicine in 2013. His exceptional skills were recognized when he received the McGraw Hill / Lange Medical Student Academic Achievement Award, and graduated top of his class with Honors. For his undergraduate degree, he attended University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) and graduated with Honors in 2009.
To further enhance his surgical expertise, Dr. Richland completed his Residency in Plastic Surgery at the University of California, Irvine (UCI) from 2013 to 2019 earning the Academic Achievement Award twice during this period. A total of 14 years in dedicated schooling and medical residency.
Dr. Richland is actively involved with healthcare and medical societies, as a Diplomate of the American Board of Plastic Surgery, a member of the American Society of Plastic Surgeons, American Society of Aesthetic Plastic Surgeons, and the California Society of Plastic Surgeons.
Contact Dr. Richland today by visiting RichlandMD.com, scheduling a cosmetic consultation, or by calling 949-867-4496 directly.










